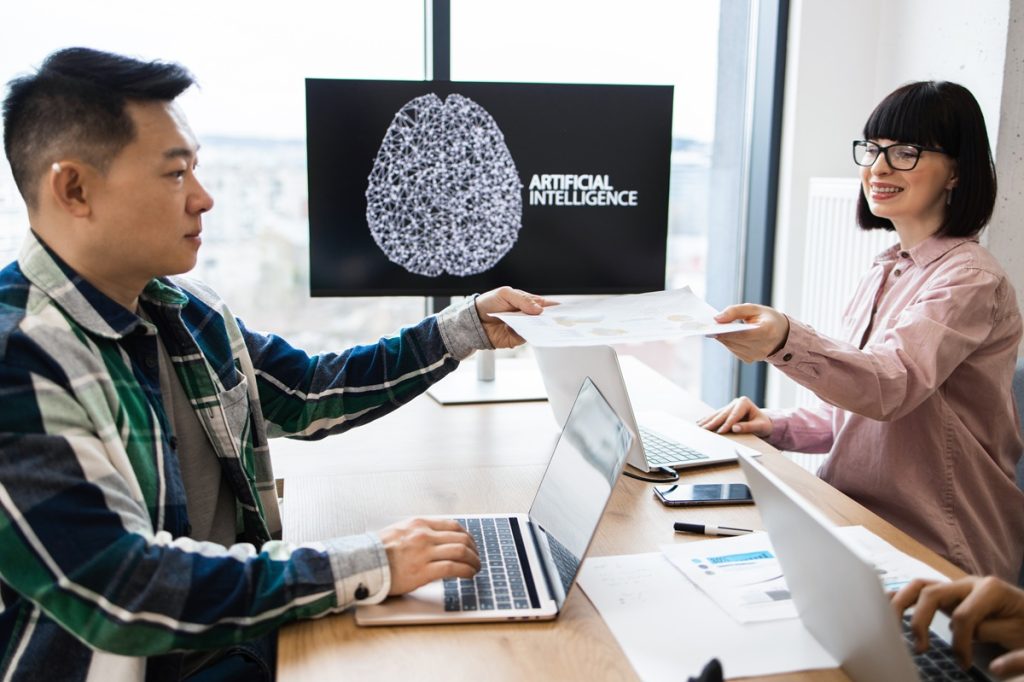
Customer service representatives play an essential role in nearly every business that interacts with customers. Whether in retail, tech, healthcare, or finance, these frontline professionals are responsible for resolving issues, answering questions, and ensuring customer satisfaction. As consumer expectations rise and digital channels expand, the role of customer service representatives (CSRs) has grown more complex—and more vital.
Customer service metrics, such as customer satisfaction, response time, and resolution rate, are increasingly used to measure the effectiveness and impact of customer service representatives.
In this guide, we’ll explore what customer service representatives do, the skills they need, the tools they use, and how they shape customer experiences. We’ll also look at how businesses benefit from investing in quality customer service and why partnering with Outsource Philippines, a top provider of customer service outsourcing, is a strategic move. Finally, we’ll preview the job outlook for customer service representatives, including industry trends and future demand.

Understanding the Role of Customer Service Representatives
A customer service representative is the face and voice of a company. They serve as the bridge between the business and the customer, answering customer questions, handling inquiries, resolving complaints, and offering guidance or technical support. But more than that, they represent a company’s values and commitment to service.
Customer service roles are diverse. Some representatives assist customers via phone, others through email, chat, or social media. Their work might involve handling routine inquiries and providing basic or scripted information, such as billing inquiries, product returns, troubleshooting, or upselling. Regardless of the task, the goal remains the same: deliver a seamless, helpful, and positive customer experience.
The Evolving Role in 2025 and Beyond
With more businesses going digital and adopting omnichannel support, CSRs are expected to be tech-savvy and emotionally intelligent. AI tools may handle repetitive tasks, but human interaction remains key in complex or sensitive situations. Customer service representatives typically are expected to:
- Resolve issues efficiently and empathetically
- Navigate CRM software and support systems
- Deliver consistent service across channels
- Collect and interpret customer feedback
Ongoing training programs are essential for CSRs to keep up with evolving technology and changing customer expectations.
Businesses that treat customer service as a cost center often miss the big picture: CSRs directly influence customer loyalty, referrals, and brand reputation.
Types of Customer Service Representatives
Customer service jobs vary depending on the business model, industry, and support channels. Here are the most common types:
- Inbound Support Representatives. Handle incoming calls, emails, or messages. They assist with inquiries, technical issues, process orders, or handle services requested by customers.
- Outbound Representatives. Make calls to follow up on customer satisfaction, conduct surveys, or promote products/services.
- Technical Support Specialists. Provide troubleshooting assistance for software, hardware, or digital products. Some technical support specialist roles are primarily installation-focused, while others handle complex troubleshooting.
- Call Center Representatives. Interact directly with customers via phone or in person, handling inquiries, complaints, orders, billing issues, and recording interactions to resolve problems efficiently.
- Customer Service Agents. Engage in direct customer interactions in call centers or in person, providing information, resolving complaints, processing transactions, and managing account details.
- Customer Support Representatives / Customer Support Reps. Interact with customers via various channels to provide information, resolve complaints, process transactions, and handle account issues.
- Client Services Representatives. Handle inquiries, resolve complaints, process transactions, and provide information about products or services, focusing on direct communication with clients.
- Member Services Representatives / Member Services Reps. Specialized customer service positions focusing on member or client engagement and support, including providing information, resolving issues, handling inquiries, and managing account-related tasks.
- Guest Service Agents. Work in hospitality settings to provide service, handle inquiries, and resolve issues for hotel or guest-related services, ensuring a positive guest experience.
- Customer Care Representatives. Provide support, handle inquiries, complaints, and service or billing issues, often across multiple customer service scenarios.
- Social Media Customer Service Agents. Monitor and respond to messages, mentions, and complaints on social media platforms.
- Live Chat Representatives. Engage customers through website chat widgets, answering questions in real-time.
- Help Desk or IT Support. Usually internal-facing, assisting employees with system issues, though some interact with clients too.
- Account Management or VIP Support. Offer premium or white-glove service to high-value clients or enterprise-level customers, often processing orders and handling services requested.
Each of these roles requires different skills and tools, but they all share a focus on understanding customer needs and creating positive experiences.
Work Environment of Customer Service Representatives
Customer service representatives work in a wide range of environments, from bustling retail stores to busy call centers and modern corporate offices. Depending on the business setting, service representatives may interact with customers face-to-face, over the phone, or through digital channels like email, live chat, and social media. The pace can be fast, and the atmosphere dynamic, especially when handling multiple customer interactions at once. Most customer service representatives work indoors in comfortable, climate-controlled spaces, but the job often comes with time pressures and the need to juggle several tasks simultaneously. Success in these environments relies heavily on strong interpersonal skills, as representatives must quickly build rapport, understand customer concerns, and resolve issues with professionalism and courtesy.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Customer Interactions
Customer service representatives wear many hats. Their typical day includes:
- Answering customer inquiries by phone, email, chat, or social media
- Obtaining details from customers to resolve inquiries and issues
- Processing orders and returns
- Documenting and updating customer records in customer relationship management (CRM) systems
- Troubleshooting and resolving customers’ problems and resolving general complaints
- Referring unresolved customer grievances to specialized departments for further investigation
- Reviewing customer insurance information and updating records as needed
- Completing contract forms and other administrative documentation
- Contacting customers for follow-up, information, or proactive outreach
- Referring customers to appropriate resources or personnel
- Processing customer bills and handling billing methods or disputes
- Maintaining financial or account records and managing financial or transactional data
- Processing other financial transactions as required
- Maintaining financial accuracy in all account and billing activities
- Using sales control systems to monitor and optimize sales processes
- Offering new or additional services to customers as appropriate
- Following scripts or knowledge bases while personalizing interactions
- Providing product/service information
- Managing upset customers with empathy and professionalism
- Maintaining performance metrics, such as response time or resolution rate
Some representatives also take on proactive tasks, like upselling or gathering feedback. The best CSRs go beyond problem-solving—they make customers feel heard, valued, and supported by working to resolve customer service issues and ensuring unresolved customer grievances are properly handled or escalated.
Must-Have Skills and Qualities
Great customer service isn’t just about following instructions—it’s about building trust and rapport. Here are the top skills employers look for:
- Communication Skills. Clear, empathetic communication is key across all platforms.
- Problem-Solving Abilities. CSRs must think on their feet and resolve issues efficiently.
- Patience and Emotional Intelligence. Staying calm under pressure makes all the difference.
- Adaptability. Each customer and situation is different; flexibility is crucial.
- Technical Proficiency. Ability to use CRM platforms, chat tools, ticketing systems, and more.
- Active Listening. Understanding customer concerns often depends on listening beyond the words.
- Time Management. Balancing multiple chats or calls requires strong multitasking skills.
- Team Collaboration. Customer support often overlaps with sales, technical, or operations teams.
- Service Orientation. A proactive attitude toward helping others and addressing customer needs effectively.
- Personal Service. Providing tailored assistance and focusing on individual customer needs to ensure satisfaction.
A solid grasp of business and management principles, along with the necessary customer service skills, is essential for professionals aiming to advance into supervisory or management roles.
Education and Training Pathways
To become a customer service representative, a high school diploma or equivalent is typically required. Many service representatives start their careers with on-the-job training, where they learn essential customer service skills such as effective communication, problem-solving, and conflict resolution. For those looking to advance or specialize, earning certifications like the Certified Customer Service Professional (CCSP) or Certified Customer Experience Professional (CCEP) can demonstrate expertise and commitment to the field. Some customer service representatives also pursue further education in business, communications, or related fields, which can open doors to customer service management roles. Whether through formal education or industry-recognized certifications, ongoing training helps representatives stay current with best practices and deliver exceptional service.
Tools and Technologies Customer Service Representatives Use
Technology empowers modern CSRs to do more with less. Common tools include:
- CRM Software (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho): Track customer interactions and history
- Help Desk Systems (e.g., Zendesk, Freshdesk): Manage tickets and knowledge bases
- Live Chat Tools (e.g., Intercom, Tawk.to): Real-time support
- Call Center Platforms (e.g., RingCentral, Aircall): VoIP and call routing
- Social Listening Tools (e.g., Sprout Social, Hootsuite): Monitor brand mentions
- AI Assistants & Chatbots: Handle basic inquiries and gather data
- Screen Sharing Tools (e.g., Zoom, TeamViewer): Used for tech troubleshooting
- Sales Control Systems: Monitor, manage, and optimize sales processes, including tracking sales performance and automating workflows
- Transactional Data Management Systems: Handle, analyze, and report on transactional data and financial or transactional data for business intelligence, financial analysis, and auditing
These tools enhance responsiveness and accuracy, but human interaction remains irreplaceable in high-stakes or emotionally charged situations.
Challenges Faced by Customer Service Representatives
The job isn’t always easy. CSRs face challenges that require patience, resilience, and strategic thinking:
- Dealing with difficult customers or aggressive behavior
- High expectations for fast responses across multiple channels
- Information overload with changing policies, products, and tools
- Burnout and emotional fatigue from repetitive tasks and stress
- Balancing personalization and efficiency
Companies that invest in training, coaching, mental wellness, and automation support can mitigate these issues and retain top talent.
Pay and Benefits
The compensation for customer service representatives varies based on factors like location, industry, and experience level. As of May 2024, the median hourly wage for a customer service representative was $20.59, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. In addition to competitive pay, many employers offer benefits packages that may include health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans. To encourage high performance and customer satisfaction, some companies provide additional incentives such as bonuses or commissions for meeting or exceeding customer satisfaction goals. Service representatives who consistently deliver outstanding results and receive positive customer feedback may also be considered for promotions or other career advancement opportunities.
Industry Variations in Customer Service Roles
The responsibilities of a customer service representative can differ greatly depending on the industry. In retail, service representatives often focus on resolving customer complaints, processing returns, and ensuring a smooth shopping experience. In the financial sector, representatives may provide technical support for online banking, answer questions about financial products, and assist with sensitive account information. Healthcare customer service representatives handle confidential patient records, review insurance policy terms, and must be knowledgeable about privacy regulations. Each industry presents unique challenges and requires specialized knowledge, making it essential for service representatives to adapt their approach and expertise to meet the specific needs of their customers.
Expert Tips to Excel in Customer Service Roles
Want to thrive as a CSR? Here are practical tips from seasoned professionals:
- Practice empathy first—validate customer feelings before offering solutions
- Be curious—ask questions to understand problems more deeply
- Master your tools—know your CRM and support platforms inside out
- Use positive language—focus on what you can do
- Follow up—customers appreciate follow-through and updates
- Keep learning—take courses in communication, product knowledge, or tech support
- Build a support network—connect with fellow CSRs to share wins and challenges
As businesses prioritize customer retention over acquisition, skilled CSRs will continue to be in high demand.
Career Advancement Opportunities
A career as a customer service representative offers numerous paths for growth and specialization. With experience and a strong foundation in customer service skills, representatives can move into roles such as team leader, supervisor, or customer service manager. Some may choose to specialize in areas like technical support or customer service management, where advanced problem-solving skills and a deep understanding of customer needs are highly valued. Opportunities also exist to transition into related fields such as sales, marketing, or human resources, leveraging the communication and interpersonal skills developed in customer service. By pursuing ongoing training and professional development, service representatives can build a rewarding career with increasing responsibility and impact on customer satisfaction.
Why Businesses Should Invest in Great Customer Support for Customer Satisfaction
Customer service representatives influence business performance more than many realize. Here’s why companies should prioritize them:
- They’re brand ambassadors. Every customer touchpoint shapes perception
- They drive retention. 89% of consumers are more likely to buy again after a positive support experience
- They gather insights. Frontline interactions provide real-time feedback on products and services
- They impact revenue. Resolving issues fast increases satisfaction and reduces churn
- They differentiate your brand. When products are similar, service is the edge
Investing in customer service includes marketing strategy considerations, as excellent support is a key component of a successful marketing strategy. Customer service not only enhances customer satisfaction but also supports the company’s overall marketing strategy by building loyalty, strengthening brand reputation, and helping to achieve business goals.
Companies that underinvest in customer service often lose ground to competitors who understand its true value.
Scale Efficiently with Expert Customer Service Representatives
If you want to scale operations without sacrificing service quality, outsourcing your customer support to Outsource Philippines is a smart, cost-effective solution. With trained, experienced CSRs, you can maintain exceptional service, 24/7 coverage, and increased flexibility—without the overhead.
Ready to enhance your customer experience? Let our experts support your business goals today.